Data science is a multidisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, techniques, algorithms, and frameworks to extract insights and understanding from structured and unstructured data. It combines information from specific domain names, including arithmetic, computer technical information, and region-specific information, to discover styles, trends, and valuable records from the data.
Major Components of Data Science
Data Collection
Example: A social media platform collects user interactions, posts, and engagement metrics to research individual behaviour.
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
Example: Removing duplicate entries, managing missing values and standardizing record formats to ensure accuracy in valuation.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Example: Using statistical strategies and visualization to understand a dataset's patterns, relationships, and outliers before formal analysis.
Feature Engineering
Example: Creating new variables or changing existing variables to boost the overall performance of the device study version.
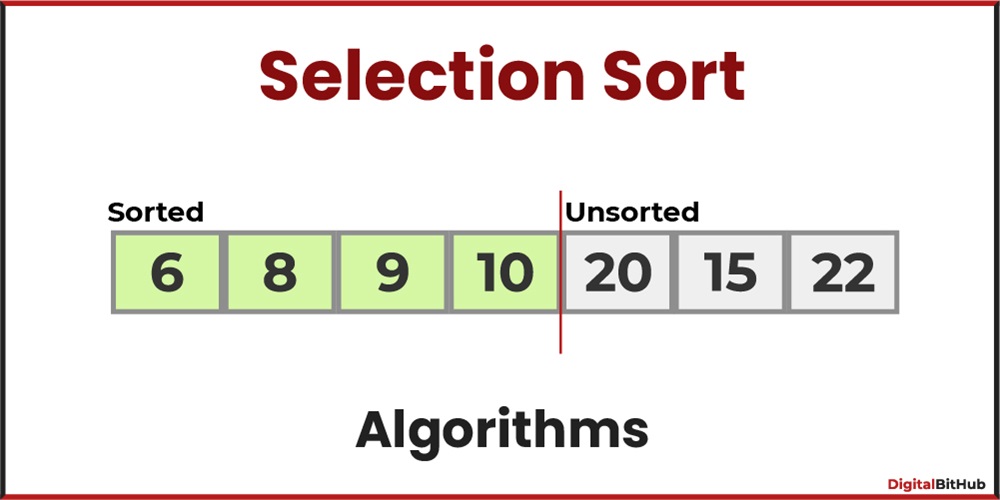
Machine Learning
Example: Training a variant to predict patron choices based on historical purchase data, allowing focused advertising strategies.
Data Visualization
Example: Creating interactive dashboards or graphs to accurately convey complex insights, including displaying stock price trends over time.
Model Evaluation and Optimization
Example: Assessing the accuracy of the predictive version and first-rate tuning parameters to improve its overall performance.
Deployment
Example: Integrating a system mastering version into a recommendation gadget on an e-trade internet site to customize product tips for customers.
Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Example: Regularly updating fraud detection structures with new facts and complex algorithms to suit the changing styles of fraud interest.
Real-World Examples of Data Science
Health Care
Example: Predicting an affected person's outcomes based on medical records and lifestyle data to optimize treatment plans and resource allocation.
Finance
Example: Analyzing economic transactions to spot unusual patterns that indicate fraudulent activities, enhancing security measures.
E-Commerce
Example: Recommendation systems recommend products primarily based on a person's behaviour, enhancing consumer experience and increasing sales.
Transportation
Examples: Using traffic data to optimize route planning, reduce congestion, and improve general site visitor control.
Marketing
Example: Analyzing customer demographics and behaviour to create focused marketing campaigns, and increase advertising ROI.
Entertainment
Example: Content advice systems on streaming platforms using target market options to customize content recommendations.
Education
Example: Analyzing student performance data to understand areas of development, allowing tailored reports.
Data Science transforms raw data into actionable insights, providing valuable solutions and improvements across various industries. It plays an essential role in shaping decision-making approaches and driving progress on a modern global scale.